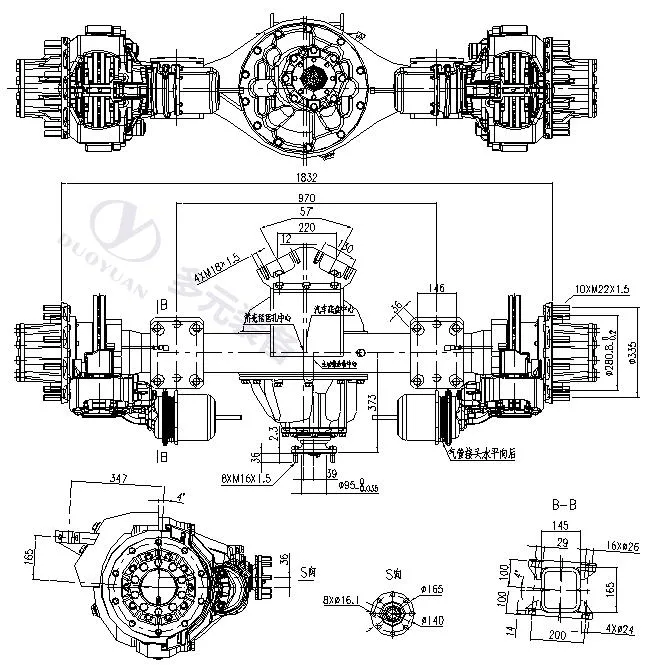
Description
Rear-Drive-Shaft
|
Suspension Model
|
AR115
|
|
|
|
Rated load(kg)
|
115000
|
Brake Type
|
Disc/Drum
|
|
Rim Distance(mm)
|
1832
|
Max out Torque(Nm)
|
30000
|
|
Distribution Circle
|
10*335
|
Flange Type
|
Plain Flange
|
|
Ratio
|
3.15~6.17
|
Applicable Bus
|
7m Bus
|
|
Wheel Hub Type
|
Bearing Unit
|
Weight(oil included)(kg)
|
690()Drum)/630(Disc)
|
Motor Drive Axle Half Shaft
A Motor drive axle half shaft is a vehicle component that transfers power from the transmission to the rear differential gearbox and then onto the wheels. It is a crucial part of a vehicle’s drivetrain because it transfers the power from the transmission to each wheel, so that the driver can steer the car.
The half shaft is a hollow metal tube with universal end joints that handles the transfer of the power from the transmission to the rear differential gearbox. This transfer of power then transfers on to the axle shaft, which runs through a perpendicular housing from the rear differential gearbox to each wheel.
They are typically fitted to rear-wheel-drive cars only and give relatively little trouble during normal motoring, although they are highly stressed components. The inner end of the half shaft is supported and driven by the differential, and the outer end is supported in bearings between shaft and axle housing. These bearings have either built-in or separate oil seals.
In some cases, the half shaft may be connected to a wheel through a bolted flange. This allows the shaft to be removed for servicing without having to remove a wheel.
CV joint boots
The constant velocity (CV) joint in a half shaft is a critical component for a drive axle to function. These CV joints are surrounded by rubber boots that keep grease in and debris out of the joints. A damaged boot can cause excessive wear on the joint, which will ultimately lead to a malfunction of the entire drive axle.
Typical symptoms of a worn half shaft include a loud click, clunk, or pop whenever the vehicle is turned. This is a common problem in vehicles with independent suspension, and it’s best to have a mechanic check the joint immediately if you notice this sound.
Another common issue that can affect the half shaft is a worn or loose shaft and pinion gears in the differential. This problem can be caused by the splines on the drive-pinion flanges being worn, causing the crown wheel and pinion gears to not mesh correctly or if the drive-flange bolts are loose.
In some instances, a damaged or loose shaft and pinion gears in a differential can be replaced with new components that will provide more robust support for the system. These replacement parts will be made specifically for the vehicle and will help prevent any further damage to the system.
These parts may be a special design or an upgrade from the existing parts on the vehicle. The new components can improve the performance of the drive axle and increase the lifespan of the drive axle.
Axle ratios
Axle ratios are an important factor in determining the vehicle’s acceleration and handling. They determine how many revolutions the drive axle turns for each wheel rotation. A higher axle ratio will result in greater acceleration, while a lower axle ratio can reduce acceleration and make the vehicle handle more gently.



